Recently, Research Center for Solar Driven Carbon Neutrality has made important progress in the field of high-entropy photothermal catalysis by synergistically enhancing the photothermal CO2 hydrogenation activity and stability of copper-based catalysts through two-dimensional high-entropy, which is coupled with the photothermal system to successfully realize high-efficiency solar-photothermal CO2 hydrogenation for the production of CO, and the related work "Cu-based high-entropy two-dimensional oxide as stable and active photothermal catalyst" was published in "Nature Communications"(2023, 14: 3171). Dr. Li Yaguang is the first author and communication author of the paper. Professor Ye Jinhua and Professor Zhang Liqiang of Yanshan University as the co-communication author.
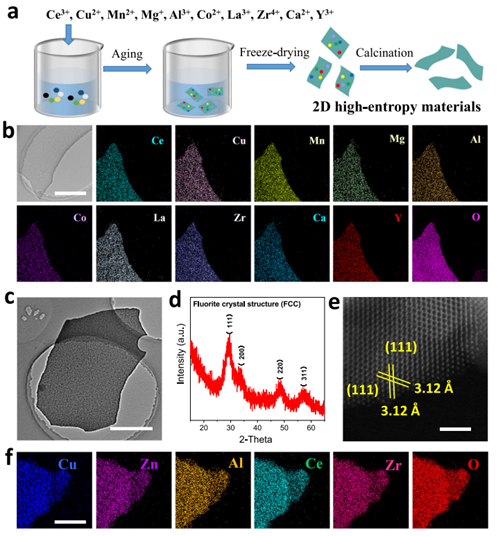
Cu-based nanomaterials are the benchmark catalysts for many photothermal catalytic applications. It is limited to the lower Taman temperature (about 400°C).Cu-based catalysts are prone to agglomerate and deactivate during high-temperature photothermal catalysis, which reduces the lifetime of the catalysts. The catalytic stability and activity of the coordinated enhancement of the copper -base light thermal catalyst is a major challenge facing. This work synthesizes six- to eleven-membered high-entropy two-dimensional (2D) materials via a polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) template method. The optimized copper-based high-entropy 2D material remains stable between 400-800°C,the performance of CO2 hydrogenation to CO reaches 417.2 mmol g-1h-1 at 500°C. Combine the copper-based high-entropy 2D materials with optical thermal devices. Under the two standard sunlight, the generating rate of light thermal catalytic CO2 hydrogenation CO reaches 248.5 mmol g-1h-1. The light-to-chemical energy conversion efficiency is 36.2%, and the outdoor optical catalytic CO output of 7 consecutive days reaches 571 L. The results show that high -entropy 2D materials provide a new path for coordinated improvement of catalyst stability and activity, and expand the scope of application of light thermal catalysis.
The above work has been funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Hebei Provincial Natural Science Foundation, the Department of Education of Hebei Province, the Institute of Life Science and Green Development of Hebei University, the research project of multi -disciplinary research projects of Hebei University, and the Hokkaido University Guangjinzi project, and Hebei The support of the Public Test Center of the School of Physics.
 Cu-based high-entropy two-dimensional oxide as stable and active photothermal catalyst.pdf
Cu-based high-entropy two-dimensional oxide as stable and active photothermal catalyst.pdf
Link: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-38889-5