Recently, Research Center for Solar Driven Carbon Neutrality has made significant progress in the field of large-scale artificial photosynthesis. The related work "A Ni-O-Ag photothermal catalyst enables 103-m2artificial photosynthesis with >17% solar-to-chemical energy conversion efficiency" was published in Science Advances (IF=13.6, 2024) with Hebei University as the main research institution. Dr. Li Yaguang is the first author and corresponding author of the paper, and Meng Qingbo, a researcher from the Institute of Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, is the co corresponding author.
Photovoltaic power generation has significant volatility, which can affect the stability of the power system. Scientists have simulated photosynthesis and developed photovoltaic electrocatalytic CO2 resource utilization technology, which uses photovoltaic electricity to drive the conversion of CO2 into chemical products. However, this technology can only achieve demonstrations on the order of 1m2, and the cost of electrode materials is relatively high. In the preliminary work, Dr. Li Yaguang and Researcher Meng Qingbo jointly proposed the idea of a new artificial photosynthesis system that couples photovoltaic electrocatalytic water splitting with photothermal CO2 hydrogenation. On this basis, Li Yaguang's research group developed a Ni-O-Ag photothermal catalyst, which enables the system to operate under low-density solar radiation. And with the support of the Institute of Life Sciences and Green Development at Hebei University, a new artificial photosynthesis system demonstration on the scale of 100 square meters was constructed.
In this work, Ag single atom is loaded on NiO nanosheets (2D Ni1Ag0.02O1). In situ DRIFTS and theoretical calculations show that the asymmetric adsorption of CO2 on 2D Ni1Ag0.02O1 enhance the activation ability of CO2, which enable the 2D Ni1Ag0.02O1 catalyst to exhibit efficient photothermal reverse water gas reaction under outdoor low-density solar irradiation. Under standard solar irradiation, the CO yield can reach 1065 mmol g-1 h-1. Based on the 2D Ni1Ag0.02O1 catalyst assisted photothermal CO2 hydrogenation system and commercial photovoltaic water electrolysis hydrogen production system, Li Yaguang's research group and Meng Qingbo's research group jointly construct an artificial photosynthesis system demonstration with a light illumination area of 103 square meters. This demonstration can eliminate dependence on the power grid and achieve fully off grid operation. Under sunlight irradiation, CO2 and H2O can be converted into green synthesis gas with a yield of~22m3/day. The H2/CO ratio can be adjusted to 0.4-3, and the average solar chemical energy conversion efficiency is 17.0%. This work demonstrates the potential application of photovoltaic photothermal coupling technology in the field of artificial photosynthesis, providing a feasible path for the deep development of light driven carbon neutrality.
The above work has received strong support from the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province, the National Natural Science Foundation, the Department of Science and Technology of Hebei Province, the Department of Education of Hebei Province, the Natural Science Multidisciplinary Research Project of Hebei University, the Research Fund Project of Hebei Agricultural University, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the Public Testing Center of the School of Physics of Hebei University.
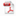 A Ni-O-Ag photothermal catalyst enables 103-m2 artificial photosynthesis with 17% solar-to-chemical energy conversion efficiency.pdf
A Ni-O-Ag photothermal catalyst enables 103-m2 artificial photosynthesis with 17% solar-to-chemical energy conversion efficiency.pdf
Link:https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adn5098